Neste tutorial você aprenderá como permitir TLSv1.3 no NGINX. O que isso significa TLSv 1.3, o que isso ajuda e porque você precisa no servidor web como TLS pode ser ativado. Para servidores com sistema de gerenciamento VestaCP (CentOS ou Ubuntu) é um pouco mais difícil ativar TLS 1.3 do que em um servidor cPanel, mas não é impossível.
Contente
Por que é melhor TLS 1.3 do que TLS 1.2?
TLS (Transport Layer Security) é um protocolo criptográfico o que garante segurança de conexão entre o computador e uma rede da qual ele faz parte. TLS é usado em aplicações como: email, mensagens, chamadas de voz e vídeo (VoIP), mas especialmente em HTTPS. Garantir a comunicação segura entre o computador ou smartphone do usuário e o servidor web da página acessada.
TLS 1.3 oferece um velocidade mais alta de conectar cliente – servidor e um Além disso segurança eliminando alguns algoritmos. As diferenças entre TLSv1.2 e TLSv1.3.
sobre HTTPS, SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) Eu também disse em outros artigos:
- Como instalar o certificado SSL (HTTPS Connection) para um site hospedado em um servidor NGINX sem cPanel ou VestaCP
- Recompilar OpenSSL 1.1 e NGINX 1.25 para TLS 1.3 (CentOS 7)
- Como mover um blog ou site WordPress de HTTP em HTTPS (Nginx)
- Excluir domínios antigos Certbot certificates (Vamos criptografar o certificado)
Como ativar o TLS 1.3 no NGINX. Servidor com gerenciamento VestaCP / CentOS
Antes de ver como ativa TLSv1.3 no NGINX, você precisa considerar alguns requisitos mínimos para TLS 1.3.
- NGINX 1.13.x ou posterior
- Um certificado TLS válido
- Nome de domínio ativo com DNS configurado corretamente – esteja acessível na Internet
- Um certificado TLS / SSL válido. Também pode ser Let’s Encrypt.
Pe VestaCP instalado há muito tempo, só temos o protocolo disponível TLS 1.2. Eu tenho visto em muitos tutoriais que é suficiente como em nginx.conf vamos adicionar a seguinte linha para ca TLS 1.3 a ser ativado:
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name example.com;
root /var/www/example.com/public;
ssl_certificate /path/to/your/certificate.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /path/to/your/private.key;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
Falso. Se servidor CentOS com gestão VestaCP, NGINX não foi compilado com a versão mínima OpenSSL 1.1.1.1, ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3; în nginx.conf .. não ajuda em nada.
[root@north ~]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.22.0
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
TLS SNI support enabledPortanto, no exemplo acima, o Nginx 1.22.0 é uma versão compatível TLS 1.3, mas a biblioteca não nos ajuda OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips.
Ativar TLSv1.3 no Nginx, primeiro você precisa instalar as bibliotecas filhas e os pacotes de desenvolvimento. Development Tools. Ele corre em CentOS 7 linhas de comando:
yum install gcc gcc-c++ pcre-devel zlib-devel make unzip gd-devel perl-ExtUtils-Embed libxslt-devel openssl-devel perl-Test-Simple
yum groupinstall 'Development Tools'1. Instale a versão mais recente OpenSSL
Neste momento, a versão mais recente é OpenSSL 1.1.1p, mas pelo que percebi já existe e OpenSSL 3. Você pode encontrar as fontes em OpenSSL.org.
cd /usr/src
wget https://www.openssl.org/source/openssl-1.1.1p.tar.gz
tar xvf openssl-1.1.1p.tar.gz
mv openssl-1.1.1p openssl
cd openssl
./config --prefix=/usr/local/openssl --openssldir=/usr/local/openssl --libdir=/lib64 shared zlib-dynamic
make -j4
make test
make install muito importante correr make test antes de instalar a biblioteca. Se o teste tiver erros, não execute make install até que os erros sejam corrigidos.
Na próxima etapa, fazemos um backup do arquivo binário atual openssl e adicionamos symlink ao novo.
mv /usr/bin/openssl /usr/bin/openssl-backup
ln -s /usr/local/openssl/bin/openssl /usr/bin/opensslEm /usr/local/openssl/bin executar ldd para verificar dependências openssl. Também podemos verificar a versão de openssl. Comando openssl version.
[root@north bin]# ldd openssl
linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007ffd20bd7000)
libssl.so.1.1 => /lib64/libssl.so.1.1 (0x00007fab09b62000)
libcrypto.so.1.1 => /lib64/libcrypto.so.1.1 (0x00007fab09675000)
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x00007fab09471000)
libpthread.so.0 => /lib64/libpthread.so.0 (0x00007fab09255000)
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007fab08e87000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007fab09df5000)
[root@north bin]# openssl version
OpenSSL 1.1.1p 21 Jun 2022Atualmente, temos a versão mais recente instalada OpenSSL que perdura TLSv1.3. Podemos verificar as versões TLS / SSL apoiado por livrarias OpenSSL por ordem:
[root@north bin]# openssl ciphers -v | awk '{print $2}' | sort | uniq
SSLv3
TLSv1
TLSv1.2
TLSv1.3
[root@north bin]# Isso não significa que sites hospedados com a ajuda do gerente VestaCP eles terão imediatamente TLS 1.3.
Embora tenhamos instalado OpenSSL 1.1.1p, o Nginx é compilado com a versão antiga OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips.
[root@north bin]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.22.0
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments: --prefix=/etc/nginx --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --modules-path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/run/nginx.lock --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/client_temp --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-compat --with-file-aio --with-threads --with-http_addition_module --with-http_auth_request_module --with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-http_random_index_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_slice_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_sub_module --with-http_v2_module --with-mail --with-mail_ssl_module --with-stream --with-stream_realip_module --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_ssl_preread_module --with-cc-opt='-O2 -g -pipe -Wall -Wp,-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -fexceptions -fstack-protector-strong --param=ssp-buffer-size=4 -grecord-gcc-switches -m64 -mtune=generic -fPIC' --with-ld-opt='-Wl,-z,relro -Wl,-z,now -pie'
[root@north bin]# openssl version
OpenSSL 1.1.1p 21 Jun 2022
[root@north bin]# 2. Recompile o Nginx para o sistema VestaCP
Nesta etapa, precisamos recompilar para OpenSSL versão do Nginx já instalada no sistema CentOS / VestaCP. Como eu disse acima, no meu caso é sobre nginx/1.22.0. Como estamos falando de um servidor web que possui VestaCP sistema de administração, antes de recompilar é bom fazer um backup dos arquivos de configuração do nginx.
Faça backup do Nginx atual no sistema VestaCP
Arquive e mantenha em algum lugar no servidor os diretórios "/etc/nginx"E"/usr/local/vesta/nginx".
CORRER nginx -V e salve os módulos existentes em um arquivo.
configure arguments: --prefix=/etc/nginx --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --modules-path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/run/nginx.lock --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/client_temp --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-compat --with-file-aio --with-threads --with-http_addition_module --with-http_auth_request_module --with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-http_random_index_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_slice_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_sub_module --with-http_v2_module --with-mail --with-mail_ssl_module --with-stream --with-stream_realip_module --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_ssl_preread_module --with-cc-opt='-O2 -g -pipe -Wall -Wp,-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -fexceptions -fstack-protector-strong --param=ssp-buffer-size=4 -grecord-gcc-switches -m64 -mtune=generic -fPIC' --with-ld-opt='-Wl,-z,relro -Wl,-z,now -pie'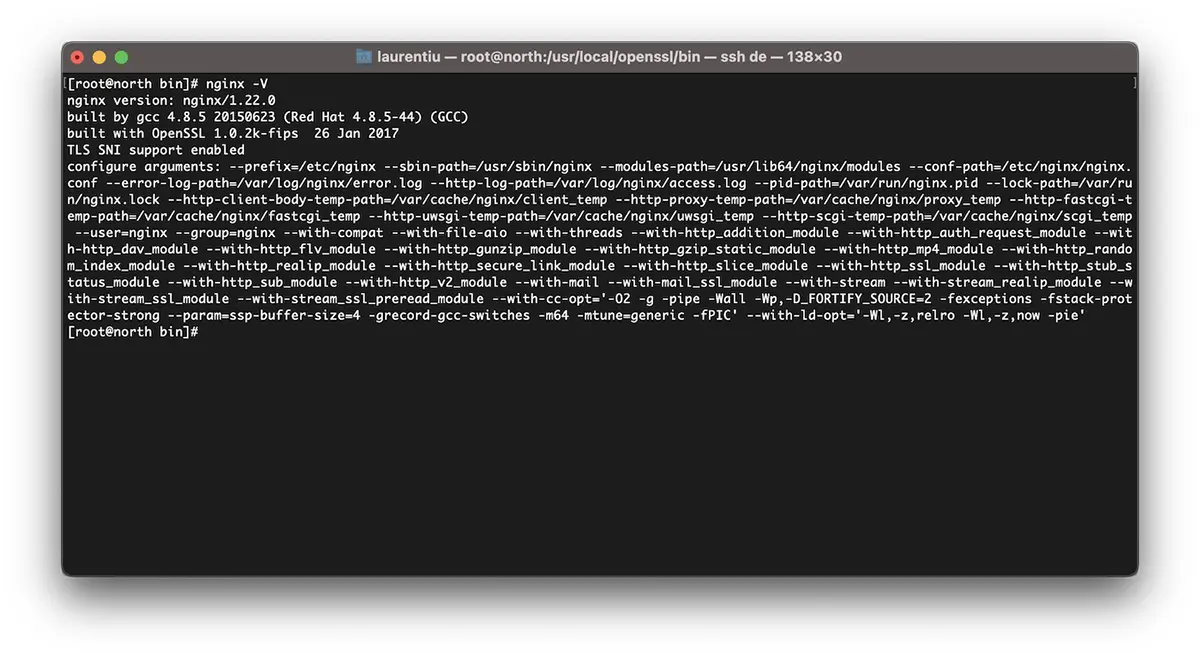
Como recompilar o Nginx para atualização OpenSSL / CentOS 7
Eu repito. Se você tem VestaCP, baixe a versão do Nginx que você já instalou. Você pode encontrar todos os arquivos com versões do Nginx em nginx.org.
cd /usr/src
wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.22.0.tar.gz
tar xvf nginx-1.22.0.tar.gz
cd nginx-1.22.0Nós recompilamos os módulos nginx:
./configure --prefix=/etc/nginx \
--sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx \
--modules-path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules \
--conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf \
--error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log \
--http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log \
--pid-path=/var/run/nginx.pid \
--lock-path=/var/run/nginx.lock \
--http-client-body-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/client_temp \
--http-proxy-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp \
--http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp \
--http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp \
--http-scgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp \
--user=nginx \
--group=nginx \
--with-compat \
--with-file-aio \
--with-threads \
--with-http_addition_module \
--with-http_auth_request_module \
--with-http_dav_module \
--with-http_flv_module \
--with-http_gunzip_module \
--with-http_gzip_static_module \
--with-http_mp4_module \
--with-http_random_index_module \
--with-http_realip_module \
--with-http_secure_link_module \
--with-http_slice_module \
--with-http_ssl_module \
--with-http_stub_status_module \
--with-http_sub_module \
--with-http_v2_module \
--with-mail \
--with-mail_ssl_module \
--with-stream \
--with-stream_realip_module \
--with-stream_ssl_module \
--with-stream_ssl_preread_module \
--with-openssl=/usr/src/openssl \
--with-cc-opt='-O2 -g -pipe -Wall -Wp,-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -fexceptions -fstack-protector-strong \
--param=ssp-buffer-size=4 -grecord-gcc-switches -m64 -mtune=generic -fPIC' \
--with-ld-opt='-Wl,-z,relro -Wl,-z,now -pie'make -j4
make installAgora temos o Nginx instalado e compilado com a versão mais recente do OpenSSL capaz de suportar TLSv1.3.
[root@north bin]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.22.0
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.1.1p 21 Jun 2022
TLS SNI support enabled*se o nginx já estiver instalado no servidor, você precisará desinstalá-lo. A compilação não está funcionando na atualização do nginx.
Como ativar o TLSv1.3 para domínios no VestaCP
no arquivo /etc/nginx/nginx.conf adicionamos as seguintes linhas:
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256';No nível do domínio, mudei algo nos modelos VestaCP e para habilitar HTTP/2. Portanto, ao adicionar um novo domínio (example.com) com o Let's Encrypt ativado, tenho o seguinte arquivo de configuração para o SSL:
cat /home/vestacpuser/conf/web/example.com.nginx.ssl.conf
server {
listen IP.IP.IP.IP:443 ssl http2;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
root /home/vestacpuser/web/example.com/public_html;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
access_log /var/log/nginx/domains/example.com.log combined;
access_log /var/log/nginx/domains/example.com.bytes bytes;
error_log /var/log/nginx/domains/example.com.error.log error;
ssl_certificate /home/vestacpuser/conf/web/ssl.example.com.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /home/vestacpuser/conf/web/ssl.example.com.key;
....
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256';Antes de reiniciar o nginx, é bom testar sua configuração primeiro.
[root@north web]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@north web]# systemctl restart nginxEspero que você ache este tutorial útil e, se estiver com alguma dúvida, deixe os detalhes do problema nos comentários.